Basaltic Magmas Are Formed by Which of the Following Processes
Magma crystallisation is a fundamental process driving eruptions and controlling the style of volcanic activity. Up to 10 cash back Basaltic magmas are formed by mantle melting and assumed to ascend along steep PT paths that approximate to adiabats eg.

A Schematic Diagram Illustrating The Magma Formation Beneath Arc And Download Scientific Diagram
By melting different parts of the layers of the earth basaltic rhyolitic and andesitic magma will be formed.
. There they crystallise and. The high pressure keeps the gas in solution in the liquid but when pressure is decreased like when you open the can or bottle the gas comes out of solution and forms a separate gas phase that you see as bubbles. Earth has a layered structure that consists of the inner core outer core mantle and crust.
1 the parent magmas of mid-ocean ridge continental flood and orogenic tholeiites which are poor in Ti and Fe rich in Al and to a lesser extent Na and 2 the parent magmas of within-plate ocean island basalts OIB which have the opposite characteristics. Magma is extremely hot liquid and semi-liquid rock located under Earths surface. We derive a set of model equations for the.
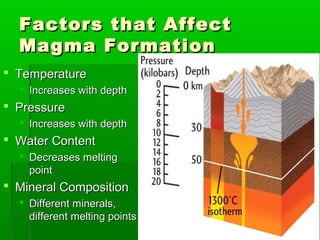
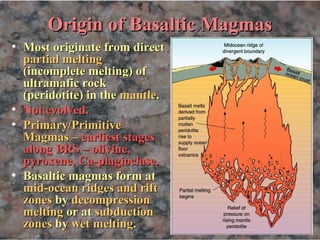
Basalt magmas form by decompression melting of peridotite in the Earths mantle a process discussed in the entry for igneous rocks. In the specific model of Collins et al. However mantle rock is ductile the solid rock slowly deforms under high stress.
The high pressure in the upper mantle due to the weight of the overlying rock raises the melting point of mantle rock so that almost all of the upper mantle is solid. Crystal nucleation delay heterogeneous and homogeneous nucleation and crystal growth are all time-dependent processes however there is a paucity of real-time experimental data on crystal nucleation and growth kinetics particularly at the. Highly hydrous basaltic magmas ascend but become trapped by a thermal boundary layer initially at around 30 km depth.
Olivine in the parental material. This process is responsible for the volcanism at mid-ocean ridges which are the most volcanically active features on earth. True Dissolved gases may comprise up to a few percent by weight of a magma.
2 What causes magma to form. Basaltic magmas have lower SiO2 contents. The rising subduction-zone magma is probably basaltic in composition and is formed by the partial melting of mantle rocks.
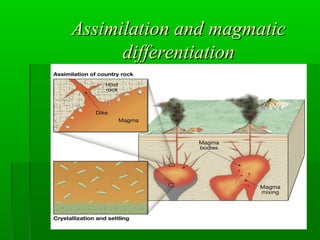
A _____ is a large volcanic depression formed by roof collapse into a partially emptied magma reservoir. As the rising magma moves slowly up through the continental crust of the overriding plate however two things may occur to increase significantly the silica content of the magma. Magma from Ancient Greek μάγμα mágma thick unguent is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed.
Which of the following processes is the last step in a volcanic eruption sequence. By partial melting of these rocks different types of basaltic magmas are formed. Composition of major basaltic magmas.
Very Fe-rich basaltic magmas may form two separate liquids - one felsic and rich in SiO 2 and the other mafic and rich in FeO. Basaltic magmas are formed by exceeding the melting point of the. Their composition depends on pressure ie depth temperature H 2 O content and degree of melting eg Green and Ringwood 1967b.
Vesicular basalt. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Initially homogeneous suspensions of bubbles in basaltic magmas and lava flows may become unstable and form rising waves or layers of bubbles.
The amount of melt relative to the parent lherzolite does not exceed ca. Much of the planets mantle consists of magma. Primitive near-primary arc magmas occur as a volumetrically minor 100 m thick unit in the Canadian Cordillera of northwestern British Columbia.
Besides molten rock magma may also contain suspended crystals and. 1 What are the 3 types of magma that commonly form volcanoes. Physicochemical constraints on melting.
Partial melting generates magmas. Different from magmas produced directly from the mantle. Magma is formed by both wet and dry melting processes.
Using data from the southern Cascade arc California USA we show quantitatively for the first. Unweathered basalt is black or gray. Plagioclase - CaAlSi3O8 to NaAlSi3O8.
On Earth most basalt has formed by decompression melting of the mantle. This magma can push through holes or cracks in the crust causing a volcanic eruption. Two main sorts of primary magmas can be identified.
Slab-derived sulfate generates oxidized basaltic magmas in the southern Cascade arc California USA Abstract Whether and how subduction increases the oxidation state of Earths mantle are two of the most important unresolved questions in solid Earth geochemistry. Thermal energy requirements for melting. Combined Processes As pointed out previously if any of these process are possible then a combination of the process could act.
Takes basaltic crust AND continental debris into the asthenosphere and lots of water. 3 What is the process that causes magma to form. Most basaltic magmas are believed to form by partial melting of granite in the lower crust and upper mantle.
Gas gives magmas their explosive character because volume of gas expands as pressure is reduced.
No comments for "Basaltic Magmas Are Formed by Which of the Following Processes"
Post a Comment